News Release
Media
Introduction to Powder Metallurgy: Understanding the Basics
Powder metallurgy (PM) is a highly versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process that plays a crucial role in modern industries. By transforming powdered materials into solid components, this technology bridges the gap between design flexibility and efficient production. This article explores the fundamentals of powder metallurgy, its processes, and its wide-ranging applications.
What is Powder Metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing technique where metal or alloy powders are compacted and sintered to create solid, precise, and durable components. The process minimizes material waste and enables the production of intricate shapes that would be challenging or costly with traditional methods like machining or casting.
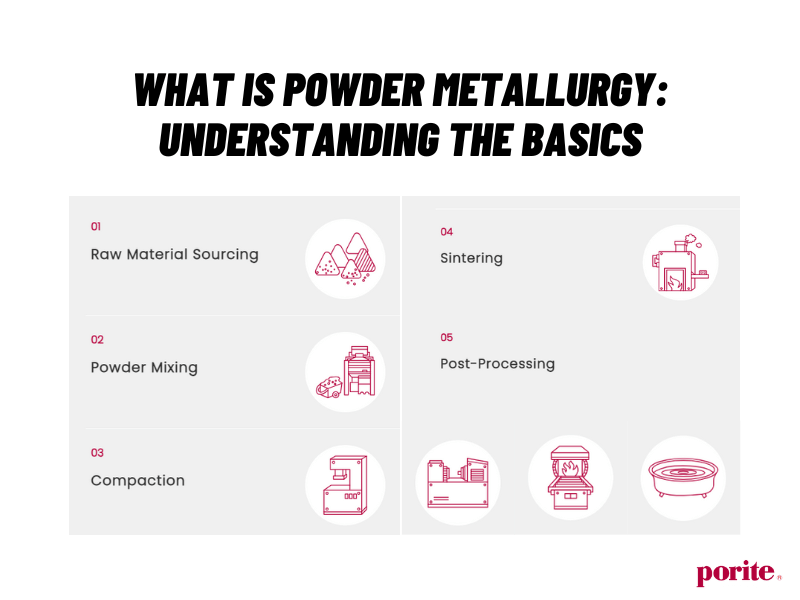
The Key Processes in Powder Metallurgy
- Raw Material Procurement: Reliable and high-quality metal raw materials are the foundation of the powder metallurgy process. Porite primarily sources raw materials from major global suppliers in Sweden and the USA, while also developing proprietary material formulations to ensure top-notch quality and precision in products.
- Powder Mixing: In addition to sourcing pre-alloyed powders, Porite has established powder mixing production lines to blend various metal powders. Lubricants and additives are included according to customer requirements to improve compressibility and sintering performance, ensuring material properties meet the specific needs of the products.
- Pressing and Shaping: This step involves compacting the metal powder into the desired shape using custom-made molds and applying pressure via forming machines. Porite’s forming machines are sourced from Germany and Japan, with pressing capacities ranging from small 5-ton machines suitable for bearings, to medium and large machines from 200 to 800 tons for automotive parts. Additionally, Porite operates Asia’s largest 1,600-ton press, continuously advancing its production capabilities.
- Sintering: Sintering is the process of densifying the shaped parts at high temperatures. During this step, powder particles diffuse and bond, forming a strong, solid structure. Sintering typically occurs at temperatures below the metal’s melting point but high enough to promote atomic diffusion and strong bonding. Porite currently operates 54 continuous sintering furnaces.
- Post-Processing: Depending on product requirements, Porite performs various post-processing operations:
- Machining and Finishing: Using machining equipment or CNC machines for shaping, grinding, and achieving precise dimensions and surface finishes.
- Heat Treatment: Includes treatments such as tempering, quenching, high-frequency hardening, and others to enhance the strength and durability of components.
Applications of Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is widely used in various industries due to its adaptability and efficiency. Some common applications include:
- Automotive: Gears, bearings, and engine components.
- Aerospace: Lightweight and high-strength parts.
- Medical: Implants and surgical instruments.
- Consumer Electronics: Magnetic and structural components.
- Industrial Machinery: Precision tools and wear-resistant parts.
Benefits of Powder Metallurgy
- Material Efficiency: PM reduces material waste, as nearly all the powder is used in the final product.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The process is ideal for high-volume production, with lower costs per unit compared to machining.
- Design Flexibility: Complex shapes and features can be achieved without extensive machining.
- Superior Performance: Components made through PM often exhibit excellent mechanical and thermal properties.
Conclusion
Powder metallurgy is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled advantages in efficiency, precision, and sustainability. As industries demand increasingly sophisticated components, PM continues to evolve and adapt, solidifying its role as a key technology for the future.
In the next article, we will delve deeper into the advantages of powder metallurgy and why it stands out in today's competitive manufacturing landscape.
